RemoveDuplicatesfromSortedArray
Question:
Given a sorted array nums, remove the duplicates in-place such that each element appear only once and return the new length.
Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Given nums = [1,1,2],
Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
It doesn’t matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
Example 2:
Given nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being modified to 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
It doesn’t matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
Clarification:
Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
Note that the input array is passed in by reference, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
Internally you can think of this:
// nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
// any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
// using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
print(nums[i]);
}
Solution 1:
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length <= 1 && nums == null ) return nums.length;
int i = 0;
for(int j = 0;j < nums.length;j++){
if(nums[j]!=nums[i]){
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
}
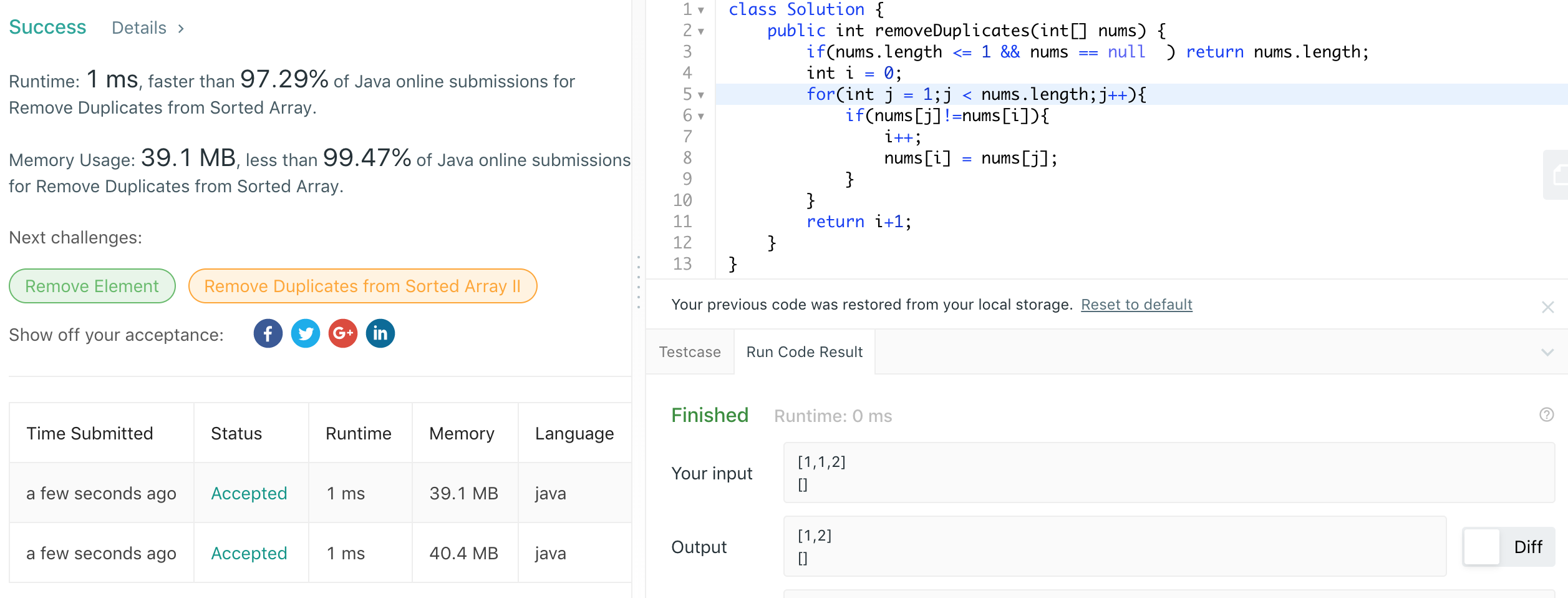
Solution 2:
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length <= 1 && nums == null ) return nums.length;
int i = 0;
// different solution1 this solution j = 0
for(int j = 1;j < nums.length;j++){
if(nums[j]!=nums[i]){
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
}
Between solution 1 and solution 2,when j begain with 1,Memory 39.1MB, so solution 2 better than solution 1.
Summary:
In computer science, an array data structure, or simply an array, is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array.
For example, an array of 10 32-bit integer variables, with indices 0 through 9, may be stored as 10 words at memory addresses 2000, 2004, 2008, … 2036, so that the element with index i has the address 2000 + 4 × i.
The memory address of the first element of an array is called first address, foundation address, or base address.
Why array begain with 0?
element with index k has the address 2000 + 4 × k.
When k = 0 ,it means that a[k] and a[0] have i offsets,If CPU caculate a[k]’s sit, Is that :
a[k]_address = base_address + k * type_size
But when array begain with 1,If CPU caculate a[k]’s sit, Is that :
a[k]_address = base_address + (k-1)*type_size
So array begain with 1,it have more Subtraction than array begain with 0.array is a basic data structure,efficiency must be excellent.
package array;
/**
* 1) 数组的插入、删除、按照下标随机访问操作;
* 2)数组中的数据是int类型的;
**/
public class Array {
//定义整型数据data保存数据
public int data[];
//定义数组长度
private int n;
//定义中实际个数
private int count;
//构造方法,定义数组大小
public Array(int capacity){
this.data = new int[capacity];
this.n = capacity;
this.count=0;//一开始一个数都没有存所以为0
}
//根据索引,找到数据中的元素并返回
public int find(int index){
if (index<0 || index>=count) return -1;
return data[index];
}
//插入元素:头部插入,尾部插入
public boolean insert(int index, int value){
//数组中无元素
//if (index == count && count == 0) {
// data[index] = value;
// ++count;
// return true;
//}
// 数组空间已满
if (count == n) {
System.out.println("没有可插入的位置");
return false;
}
// 如果count还没满,那么就可以插入数据到数组中
// 位置不合法
if (index < 0||index > count ) {
System.out.println("位置不合法");
return false;
}
// 位置合法
for( int i = count; i > index; --i){
data[i] = data[i - 1];
}
data[index] = value;
++count;
return true;
}
//根据索引,删除数组中元素
public boolean delete(int index){
if (index<0 || index >=count) return false;
//从删除位置开始,将后面的元素向前移动一位
for (int i=index+1; i<count; ++i){
data[i-1] = data[i];
}
//删除数组末尾元素 这段代码不需要也可以
/*int[] arr = new int[count-1];
for (int i=0; i<count-1;i++){
arr[i] = data[i];
}
this.data = arr;*/
--count;
return true;
}
public void printAll() {
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
System.out.print(data[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array array = new Array(5);
array.printAll();
array.insert(0, 3);
array.insert(0, 4);
array.insert(1, 5);
array.insert(3, 9);
array.insert(3, 10);
//array.insert(3, 11);
array.printAll();
}
}